

Simlocks have completely vanished from the market at least here in Germany, mostly because carriers don’t care if you use your subsidised bonus phone with a different card – you’re still locked into a contract with two years or such minimum duration. Even those contracts have gotten rare though I think most people right-out own their phones and then make a separate contract.






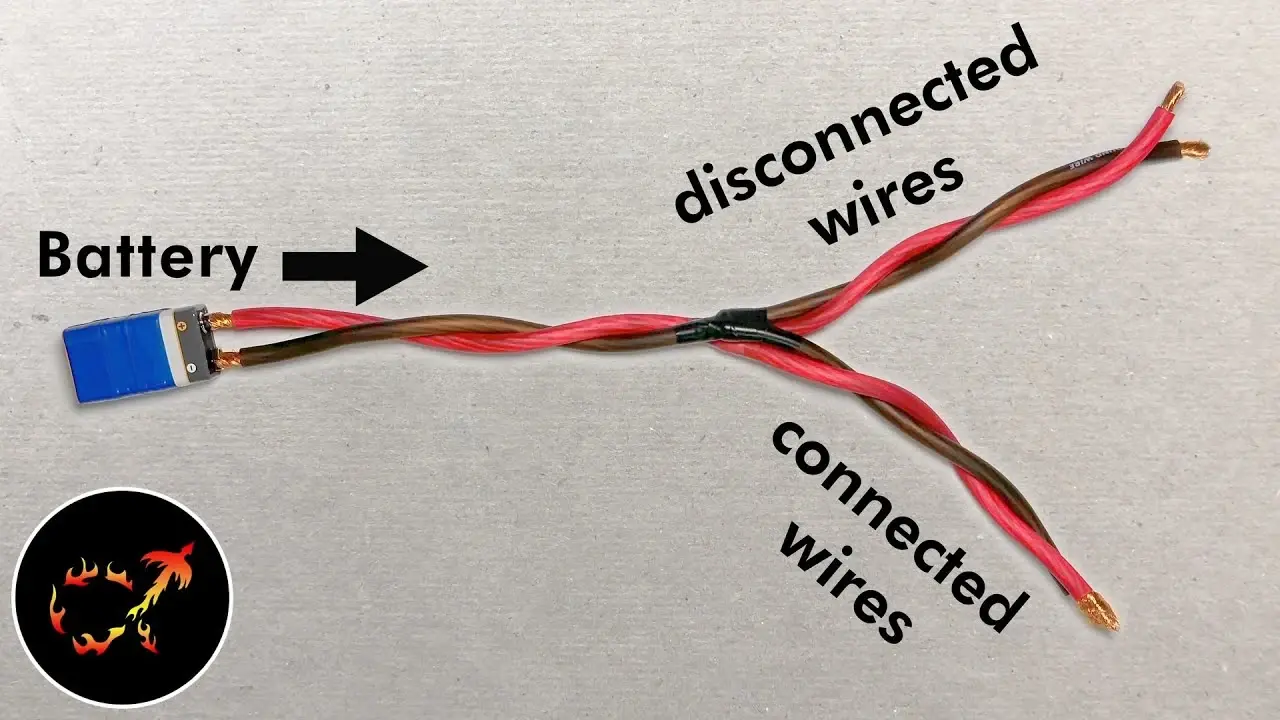




They’ve definitely done that before, dunno if it was deliberately. They must have somewhat of an idea how long it takes for nocebo to kick in with the local village idiots, if it’s short enough it could actually be a rather good idea to make waiting a bit a general policy. Tank some mild capital and opportunity cost to prevent having to battle in court and the town newspaper? Sounds like a win to me.